 Junit тестирование
, как правильно создавать модули к коду
Junit тестирование
, как правильно создавать модули к коду
 |
Наши проекты:
Журнал · Discuz!ML · Wiki · DRKB · Помощь проекту |
|
| ПРАВИЛА | FAQ | Помощь | Поиск | Участники | Календарь | Избранное | RSS |
| [216.73.216.250] |

|
|
 Следующие правила действуют в данном разделе в дополнение к общим Правилам Форума
Следующие правила действуют в данном разделе в дополнение к общим Правилам Форума
1. Здесь обсуждается Java, а не JavaScript! Огромная просьба, по вопросам, связанным с JavaScript, SSI и им подобным обращаться в раздел WWW Masters или, на крайний случай, в Многошум.
2. В случае, если у вас возникают сомнения, в каком разделе следует задать свой вопрос, помещайте его в корневую ветку форума Java. В случае необходимости, он будет перемещен модераторами (с сохранением ссылки в корневом разделе).
3. Запрещается создавать темы с просьбой выполнить какую-то работу за автора темы. Форум является средством общения и общего поиска решения. Вашу работу за Вас никто выполнять не будет.
4. Не рекомендуется создавать несколько несвязанных вопросов в одной теме. Пожалуйста, создавайте по одной теме на вопрос.
2. В случае, если у вас возникают сомнения, в каком разделе следует задать свой вопрос, помещайте его в корневую ветку форума Java. В случае необходимости, он будет перемещен модераторами (с сохранением ссылки в корневом разделе).
3. Запрещается создавать темы с просьбой выполнить какую-то работу за автора темы. Форум является средством общения и общего поиска решения. Вашу работу за Вас никто выполнять не будет.
4. Не рекомендуется создавать несколько несвязанных вопросов в одной теме. Пожалуйста, создавайте по одной теме на вопрос.
Модераторы: dark_barker, wind
 Junit тестирование
, как правильно создавать модули к коду
Junit тестирование
, как правильно создавать модули к коду
|
Сообщ.
#1
,
|
|
|
|
Разбираюсь с Junit в Eclipse. Eсть LRU и LFU алгоритмы с вложенными классами. Вот LRU класс:
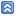  package Main; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.Map; public class LRUAlgoritm<K, V> implements Cache<K, V>{ private LRUStorage storage; public LRUAlgoritm(int capacity) { this.storage = new LRUStorage(capacity); } @Override public V get(K key) { return storage.get(key); } @Override public V put(K key, V value) { return storage.put(key,value); } private class LRUStorage extends LinkedHashMap<K, V>{ private final int capacity; private LRUStorage (int capacity){ this.capacity = capacity; } @Override protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K, V> eldest){ return size()>capacity ; } } @Override public String toString() { return "storage= " + storage ; } } Вот LFU класс:   package Main; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Objects; public class LFUCache<K, V> implements Cache<K, V> { private final LinkedHashMap<K, Node> storage; //the declaration of the variable "storage" for storing data with key type "K" and value type "Node". private final int capacity; public LFUCache(int capacity) { if (capacity <= 0) {//validation of the capacity on the negative and the zero value throw new IllegalArgumentException("Capacity should be more than 0"); } this.capacity = capacity; this.storage = new LinkedHashMap<>(capacity, 1); //initialization of variable "storage" - data storage. //Inside the parentheses: the specified initial capacity and load factor = 1 } //overriding methods "get" and "put" to be implemented from the interface "Cache" @Override public V get(K key) { Node node = storage.get(key);//the get method of LinkedHashMap class according to the //"http://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/util/LinkedHashMap.html" //returns "null" if the requested key is missing or //has the value - a Hash mapping key if the key exists in the cache storage "storage" if (node == null) {//check the value of the variable "node" to NULL return null; } return node.incrementFrequency().getValue();//if the value of the variable "node" is not NULL, //then the called method to increase the frequency on the unit and //obtain take associated with the key "key" variable value "value" } @Override public V put(K key, V value) { // if (storage.get(key)!=null&& Objects.equals(value, storage.get(key).getValue())) //{return storage.get(key).incrementFrequency().getValue();}//verification of the presence of the led element in the cache storage "storage" //if the element is present then return the value from the cache store doEvictionIfNeeded(key);//verification of occupancy of the cache storage, and the presence of the inserted key in the cache storage "storage" Node oldNode = storage.put(key, new Node(value));//the put method, inherited from Map interface, returns the previous value associated with key, //or null if there was no mapping for key if (oldNode == null) { return null; } return oldNode.getValue(); } // method to displace the old value with the least frequency when the storage of the cached data is completely filled private void doEvictionIfNeeded(K putKey) { if (storage.size() < capacity) {//verification of occupancy of the cache storage return; } long minFrequency = Long.MAX_VALUE;//the maximum assignable value for a variable of type Long K keyToRemove = null; for (Map.Entry<K, Node> entry : storage.entrySet()) {//search cash store the minimum value of frequency the "frequency" of all those elements if (Objects.equals(entry.getKey(), putKey)) { //no eviction required cause element already exists, we just need to replace it return; } if (minFrequency >= entry.getValue().getFrequency()) { minFrequency = entry.getValue().getFrequency(); keyToRemove = entry.getKey(); } } storage.remove(keyToRemove);//removal item's key with the minimum number of calls } //an inner class "Node" in the object which is stored the value "value". //And is created for this value a variable to hold the frequency "frequency" to the value "value' private class Node { private final V value; private long frequency; //create a constructor with a parameter (a value of type V) to write the value in the node object. //And setting the initial value of the frequency of reference to "value" - "frequency" = 1 public Node(V value) { this.value = value; this.frequency = 1; } public V getValue() { return value; } public long getFrequency() { return frequency; } public Node incrementFrequency() {// method to increase frequency by one(+1) ++frequency; return this; } @Override public String toString() { return "Node [value=" + value + ", frequency=" + frequency + "]"; } } @Override public String toString() { return "storage = "+ storage + ", capacity=" + capacity ; } } Для LRU алгоритма я сделал тест класс для класса LRUStorage IDE сгенерировала код класса с одним единственным методом:   package Test; import static org.junit.Assert.*; import org.junit.Test; public class TestLRUAlgoritm { @Test public final void testRemoveEldestEntryEntryOfKV() { fail("Not yet implemented"); } } Каким образом его теперь протестировать? метод removeEldestEntry() это переопределенный метод LinkedHashMap ? какие значения ему отдавать, что бы они адекватны для тестирования? Пересмотрел и Ткача, Немчинского и Владыкина на простых примерах какие данные передать и какой ассерт взять понятно(добавляем 2 и 2 и ждем 4), здесь же голову сломал, кучу статей перечитал ничего не понимаю, помогите разобраться? я только пытаюсь разобраться, что нужно теститровать и какую именно функциональность необходимо тестировать. В моем примере (class LRUAlgoritm) есть три метода во внешнем классе LRUAlgoritm (get, put, toString) и один во внутреннем классе LRUStorage (remove Eldest Entry). Все они переопределенные. Нужно ли тестировать их логику? Ведь по правилам нужно покрывать тестами 100% кода? Если да, то какие параметры и что на выходе тогда должно быть? второй класс дан как разъяснение других примеров, для наглядности. |
1 пользователей читают эту тему (1 гостей и 0 скрытых пользователей)
0 пользователей:
[ Script execution time: 0,0262 ] [ 14 queries used ] [ Generated: 2.07.25, 14:25 GMT ]


